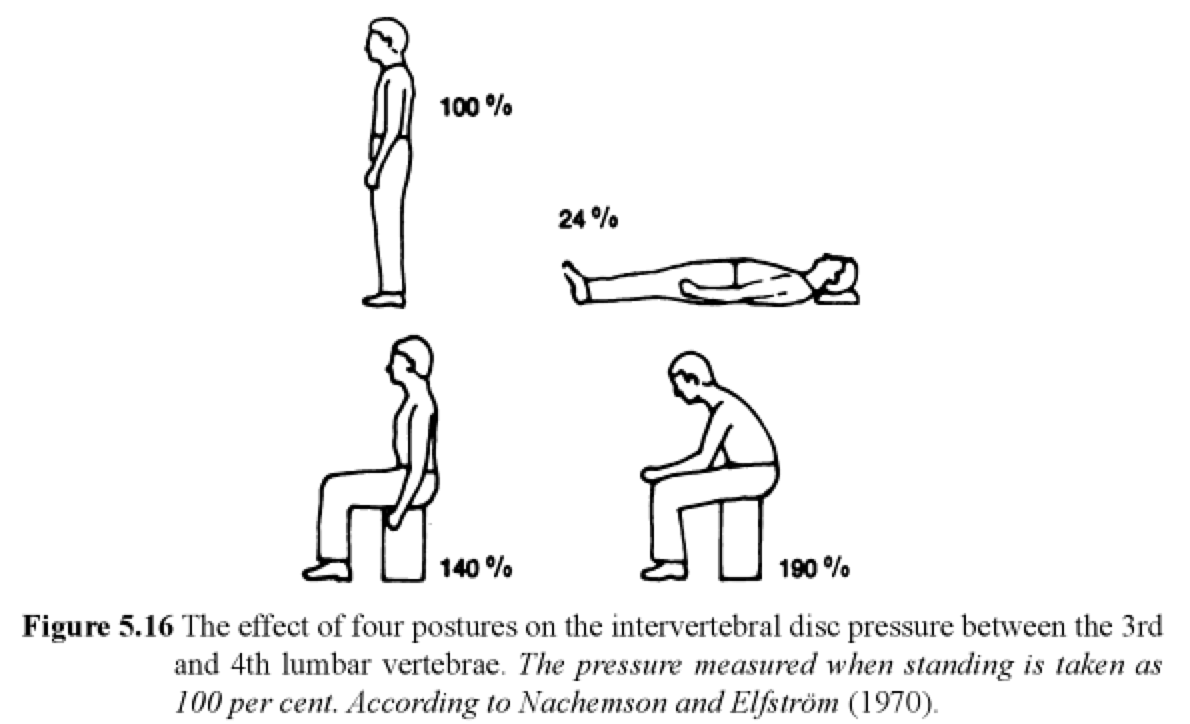
You’ve likely heard that sitting is the new smoking. That’s because too much sitting can harm your health and place stress on your body. Did you know that sitting adds a strain up to 1.5x your body weight, compared to standing? In addition, there is an increased rate of strain, up to 2x your body weight, particularly in those with poor posture, body mechanics, and incorrect ergonomic setups.
Is your desk setup causing you neck strain, low back pain, carpal tunnel syndrome, or hand and wrist tendinitis? Muscles, tendons, ligaments, nerves, and blood vessels are being compressed when you remain in the same position for an extended period.

It is essential to change position between sitting and standing every 30 minutes; but when you are in the seated position, it is even more important that you have the proper ergonomic setup to support your
“good posture.”
Sitting With Good Posture
You have probably been told before, “sit with good posture,” but what does that exactly mean?
Sit back in your chair until your low back feels supported, or pressed against the lumbar support (extra cushion in the low back region). Squeeze shoulder blades together.
Slouching and slumping put increased pressure on the intervertebral discs, leading to increased low back pain.
How to Position Your Body While Sitting
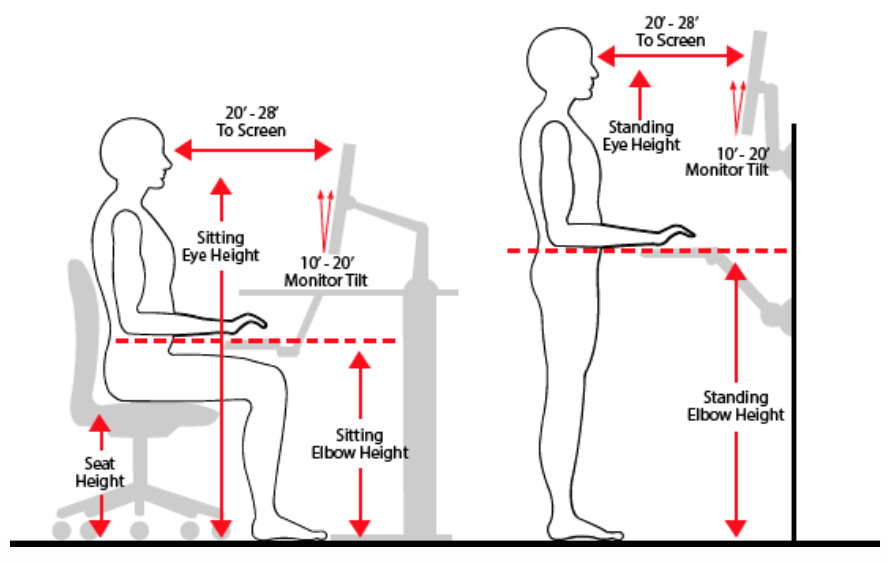
1. Keep your head level.
2. Relax your shoulders.
3. Support your low back.
4. Place your elbows at your sides—bent at 90-100 degree angle when typing.
- Placing the arms too high can put increased stresses on your shoulder joints and upper back.
- Refrain from leaning and putting too much pressure on your elbows.
5. Keep wrists straight in a neutral position
6. Maintain hips at a 90-degree angle.
7. Ensure your thighs are parallel to the floor or slightly downward.
8. Bend knees at a 90-degree angle with a 2-inch space (or a fist-width) between the back of your knees and the seat pan.
- This will allow proper blood circulation to the lower extremities and prevent any compression essential vascular structures.
9. Keep feet supported and planted on the floor—consider using a footstool to rest your feet to achieve this position if the chair is not adjustable.
Choosing an Ergonomic Chair
Here are some features to look for in an ergonomic chair:
- Comfortable cushion—gel cushions and memory foam cushions are most supported
- Adjustable lumbar support—decreases stress on the upper body and low back
- Recline capability—reduces stress on the discs
- Adjustable seat height—this will allow you to adjust it to the appropriate knee bend while maintaining both feet flat on the floor
- Swivel—ability to rotate, so you don’t strain your body trying to twist and reach other areas of the desk space
How to Set up Your Monitor and Screen
- Your monitor should be approximately 20-28 inches (1 arm’s length) from you.
- Extend your arm to where your middle finger can touch the screen.
- Tilt the top of the monitor back 10 to 20 degrees.
- The top of the viewing screen should be at eye level when you are sitting with good posture in an upright position.
- Your eyes should be in line with the address bar
*This is important, not only to avoid neck fatigue and shoulder tension but also to prevent strain on the eyes.*
How to Position Your Keyboard and Mouse
- Place keyboard close to you to avoid excessive reaching and rounded shoulder position.
- The mouse should be the same height of the keyboard and the wrist should be in a neutral position.
- When you aren’t using the mouse, rest your hand in your lap. Doing so will help to avoid excessive wrist extension, which compresses important wrist structures.
Other Helpful Tips
Create support. If you do not have a lumbar support on your chair, no problem! You can create your own. Simply roll up a small towel or sweater. Place it between the curve in the small of your back. The same goes for those long car drives or flights on a plane.
Give your body some backing. If your desk is too high to have proper chair settings, raise the chair up, and use a footrest or piled books to support the feet so that you can achieve proper upper body ergonomics as well.
Avoid stashing stuff under your desk. Storing items under your desk often leads to unwanted body mechanics when reaching for those items and limits your ability to stretch your legs throughout the say.
Don’t scrunch your shoulders. Avoid hunching your shoulder to hold a phone to your ear.
Contact Us Today
If you have other questions about office ergonomics, give our practice a call. Chiropractic adjustments also can keep your spine aligned so you can work without discomfort.
References:
- https://www.athletico.com/2014/02/26/sitting-v-standing/
- https://lifehacker.com/the-science-behind-posture-and-how-it-affects-your-brai-1463291618
- https://www.vastmarket.com/blog/should-i-sit-or-should-i-stand-maybe-both/?utm_medium=social&utm_source=facebook&utm_content=headerad&utm_campaign=facebookads
By: Carly Stote
